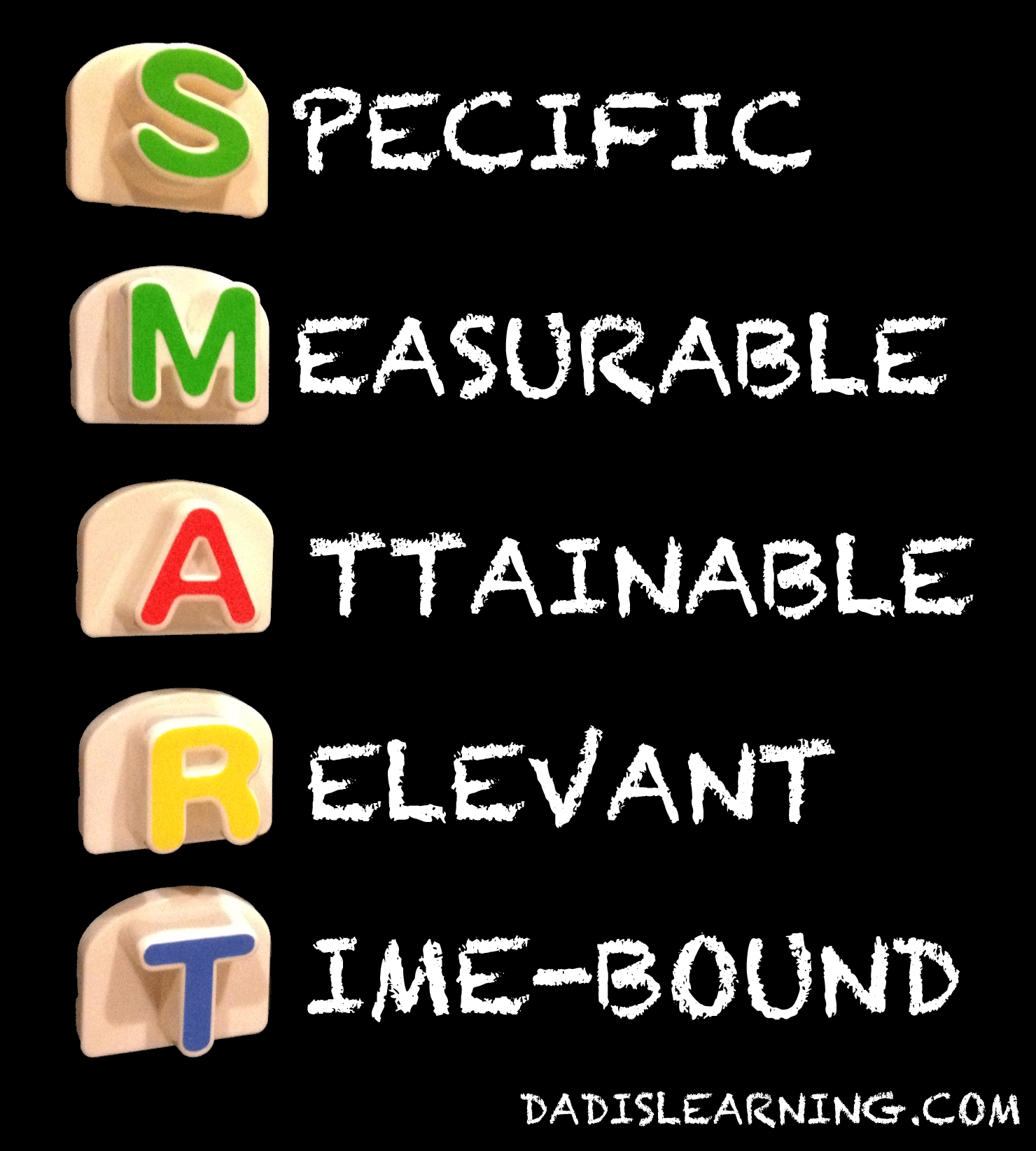Goal
Setting: A Plan to Avoid Failure….
Somebody
has rightly said that, “Failing to Plan is the same as Planning to Fail”. The
sole reason for life is to achieve a goal, be it financial, career, family or
social
What is
a Goal?
The end
toward which effort is directed. Goals are dreams and wants except a goal is
more specific.
The
Purpose of Goals
The purpose
of goals is to give you something that you want to enhance your life in some
way, so the most important thing you need to know about goals is that you ought
to have some.
Types of
Goals
Long
Term Goals:
10-year, 5-year and 1-year goals
10-year, 5-year and 1-year goals
Short
Term Goals:
goals for the next 9 months, 6 months and 3 months
goals for the next 9 months, 6 months and 3 months
Immediate
Goals:
1-30 days from now
1-30 days from now
"TIME
IS LIFE. TO WASTE YOUR TIME IS TO WASTE YOUR LIFE; TO MANAGE YOUR TIME IS TO
MANAGE YOUR LIFE." -- ALAN LAKEIN
How to
Set Goals
Learning
how to set goals is as important as knowing what the goal should contain.
What’s important to remember about setting goals is the correct F.R.A.M.E. of
mind. What is meant by “frame of mind?” Each letter in the word
“frame” illustrates the following:
F.R.A.M.E
Fantasize
- Dream your
wildest dreams and make sure that your goals match your values. Ask yourself:
what do you want to be doing in 1 year? 5 years? What kind of person do I want
to be?
Reality - Fantasies can become reality,
depending on how hard you are willing to work for them.
Aim - Define your goal(s) by striking a
balance between Fantasy and Reality; set a high but realistic goal.
Method – Be truthful to yourself by
narrowing your choices or goals to the ones you really intend to
accomplish. Don’t be afraid to ask for
help.
Evaluation
- Process the results,
but don’t make it the last step; evaluation should be on going.
Goal
setting works!!!!!!
Goal setting helps you to identify what you want to accomplish and
find a way to do it.
5
Qualities of Effective Goals
S.M.A.R.T.
Before you
begin your goal setting process it is important to know what qualities your
goals should embody. Effective goals have three important qualities. They are
realistic, measurable, and reviewed.
SPECIFIC
The Goal
should be SPECIFIC enough so that we know exactly for what we are
striving.
MEASURABLE
A goal must
be MEASURABLE. It should have concrete facts. You should be able to
answer very specifically, when and how you will know you attained your goal.
ACTION
ORIENTED
ACTION-ORIENTED,
declaring positive activity that will produce
results.
REALISTIC
A goal must
be REALISTIC. Challenging yourself is an important part of goal setting.
You want to aim high; however, you also need to be realistic.
TANGIBLE
TANGIBLE meaning concrete and not vague.
Goals must also be…
REVIEWED
Finally, a
goal must be REVIEWED.
Share your
goals with friends and family members who care about your success. Pick one of
these persons who will hold you accountable in addition to yourself. In the
meantime, remind yourself regularly of the goals you have set for yourself.
Steps
Toward Setting Effective Goals
"
THE ESTABLISHMENT OF A CLEAR AND CENTRAL PURPOSE OR GOAL IN LIFE IS THE
STARTING POINT OF ALL SUCCESS." -- BRIAN TRACY
1. Set
Goals
Identify
what is important to you. What do you want to accomplish?
2.
Identify possible strategies or objectives to reach each goal.
Make a list
of what you feel are the best and most effective ways of reaching the goals you
have already identified.
3.
Select the best strategies
Now that
you have made a list of several ways to achieve your goal, recognize which of
these strategies will work best for you.
4.
Outline specific plans to accomplish each strategy.
Once you
have narrowed down your strategy list, you can begin to make very detailed and
specific plans to accomplish each strategy and ultimately reach your goal.
Once we
have a well-formed Goal Statement we need some direction to follow to achieve
this Goal.
"AN
UNWRITTEN WANT IS A WISH, A DREAM, A NEVER HAPPEN. THE DAY YOU PUT YOUR GOAL IN
WRITING IS THE DAY IT BECOMES A COMMITMENT THAT WILL CHANGE YOUR LIFE. ARE YOU
READY?" - TOM HOPKINS
Setting
goals is a means of identifying and plotting how you are going to achieve your
aims in life. By writing down your goals you are committing yourself to accomplishing
them; therefore, make sure that your goals are important to YOU!!!!!
Motivation
Motivation
and commitment are what make us strive to achievement. They give us the push,
desire, and resolve to complete all of the other steps in the Goal process.
This
motivation can be obtained by developing a personal statement that creates a
high level of emotion and energy that guarantees achievement.
Motivation
Story
Once Jamsetji
Tata was not allowed in a Five Star Hotel in Mumbai, in future he went on to
Build Hotel Taj, a monumental building. The
motivation of being asked to leave the hotel provided the necessary fuel for
him to achieve this goal.
Commitment
Commitment
creates more accountability and is what sets us on direct course to reach our
goals. It may create costly negative consequences upon failure to attain a
goal.
Making a
commitment might be something like having invested your savings in your new
business which you will lose if it fails. Motivation and commitment are specific
to your situation and life and only you can form statements that will ensure
you reach your goal the quickest.
The more
personal you make your motivation and commitment statements for each goal, the
more motivated you will be to accomplish your goal.
BE FLEXIBLE
Be ready to
re-adjust your goals and not give up on them. If they are too easy, they won't
be worthwhile, and if they are too tough, and you will start thinking that the
idea of goal setting is worthless. Remember, small victories lead to big
successes.
Why
Goals Fail
Ø
The
goal was not written down.
Ø
Rewards
for achieving the goals were not given.
Ø
The
goal was unrealistic or not specific enough.
Ø
The
goal is not really believable or little commitment exists.
Ø
Keep
changing or switching goals with the weather
Ø
The
person who set the goal has not told anyone else for added accountability, help
and support.
Ø
The
goal was not incorporated into a realistic plan that includes measurements,
timelines and resources.
The
Benefits of Setting Goals
Ø
Suffer
less from stress and anxiety
Ø
Concentrate
better
Ø
Show
more self-confidence
Ø
Perform
better
Ø
Are
happier